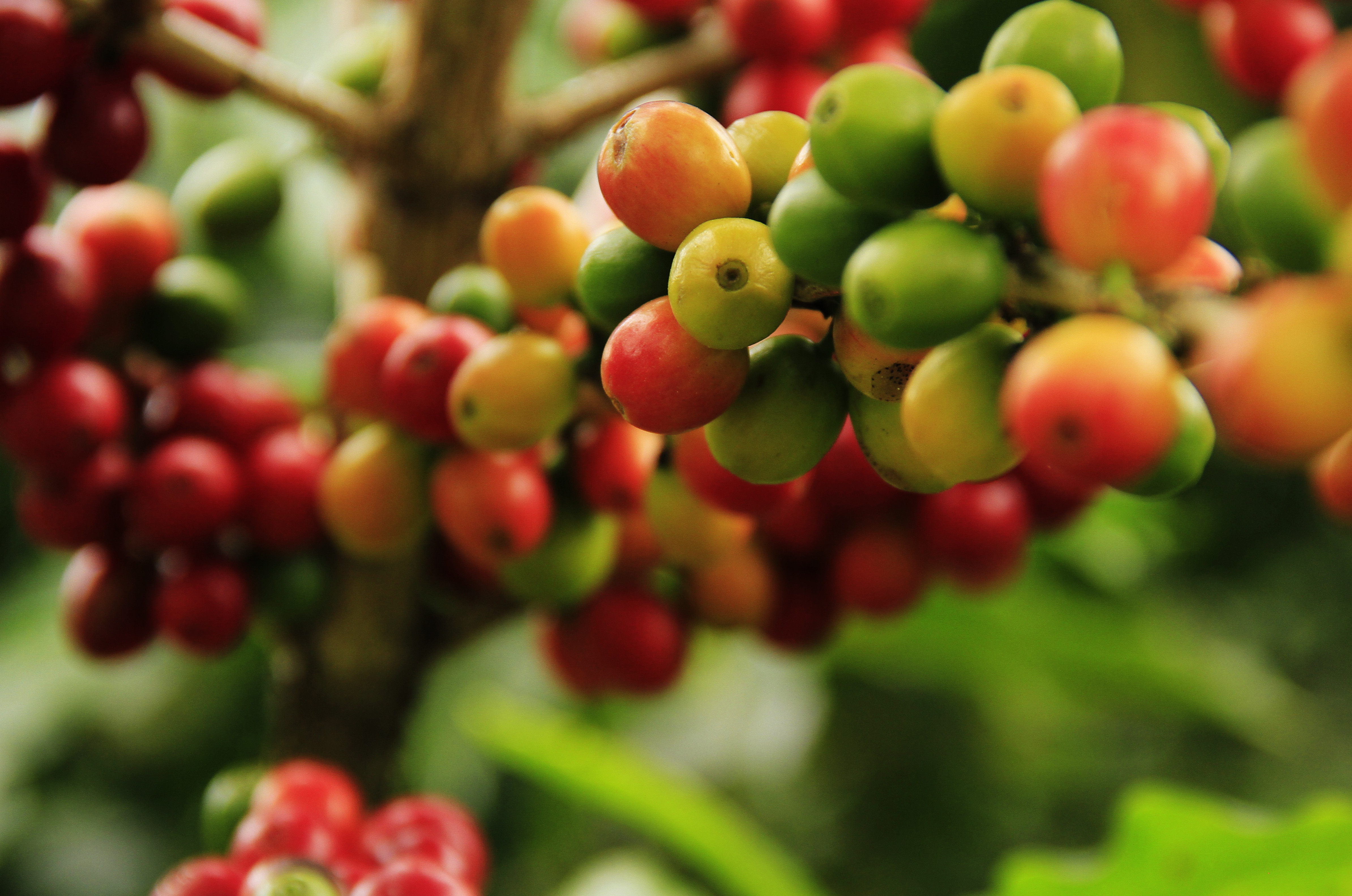
Bem vindo à Biblioteca do Café
O SBICafé é um repositório temático da produção científica das instituições que integram o Consórcio Brasileiro de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento do Café (Consórcio Pesquisa Café). Seu objetivo é unificar e facilitar o acesso à produção científica das instituições consorciadas, no que se refere a temas relacionados ao agronegócio do café, aumentando assim a visibilidade, o uso e o impacto dos resultados das pesquisas depositadas, no intuito de fortalecer os projetos desenvolvidos em torno do Programa Nacional de Pesquisa e Desenvolvimento do Café (PNP D/Café), aumentando sua produtividade, progresso e recompensas.

Seções no SBICafé
Selecione uma seção para navegar por suas coleções
Submissões Recentes
Incidence and distribution of filamentous fungi during fermentation, drying and storage of coffee (Coffea arabica L.) beans
(Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia, 2008-10-02) Silva, Cristina Ferreira; Batista, Luis Roberto; Schwan, Rosane Freitas
The objective of this work was to isolate and characterize filamentous fungi present in different stages of harvest, fermentation, drying and storage of coffee beans processed by natural method. The cherries were hand-picked and then placed on a cement drying platform where they remained until reached 11% of humidity. Microbial counts were found in all samples during fermentation and drying of the coffee beans. Counts of fungi in the coffee cherries collected from the tree (time 0) were around 1.5 x 10³ CFU/g. This number increased slowly during the fermentation and drying reaching values of 2 x 10(5) CFU/g within 22 days of processing. Two hundred and sixty three isolates of filamentous fungi were identified. The distribution of species during fermentation and drying was very varied while there was a predominance of Aspergillus species during storage period. The genera found were Pestalotia (4), Paecelomyces (4), Cladosporium (26), Fusarium (34), Penicillium (81) and Aspergillus (112) and comprised 38 different species.
Ochratoxigenic fungi associated with green coffee beans (Coffea arabica L.) in conventional and organic cultivation in Brazil
(Sociedade Brasileira de Microbiologia, 2013-10-09) Rezende, Elisângela de Fátima; Borges, Josiane Gonçalves; Cirillo, Marcelo Ângelo; Prado, Guilherme; Paiva, Leandro Carlos; Batista, Luís Roberto
The genera Aspergillus comprises species that produce mycotoxins such as aflatoxins, ochratoxins and patulin. These are cosmopolitan species, natural contaminants of agricultural products. In coffee grains, the most important Aspergillus species in terms of the risk of presenting mycotoxins belong to the genera Aspergillus Section Circumdati and Section Nigri. The purpose of this study was to assess the occurrence of isolated ochratoxigenic fungi of coffee grains from organic and conventional cultivation from the South of Minas Gerais, Brazil, as well as to evaluate which farming system presents higher contamination risk by ochratoxin A (OTA) produced by fungi. Thirty samples of coffee grains (Coffea arabica L.) were analysed, being 20 of them of conventional coffee grains and 10 of them organic. The microbiological analysis was done with the Direct Plating Technique in a Dichloran Rose Bengal Chloramphenicol Agar (DRBC) media. The identification was done based on the macro and micro morphological characteristics and on the toxigenic potential with the Plug Agar technique. From the 30 samples analysed, 480 filamentous fungi of the genera Aspergillus of the Circumdati and Nigri Sections were isolated. The ochratoxigenic species identified were: Aspergillus auricoumus, A. ochraceus, A. ostianus, A. niger and A. niger Aggregate. The most frequent species which produces ochratoxin A among the isolated ones was A. ochraceus, corresponding to 89.55%. There was no significant difference regarding the presence of ochratoxigenic A. ochreceus between the conventional and organic cultivation systems, which suggests that the contamination risk is similar for both cultivation systems.
Atrativo para as abelhas Apis mellifera e polinização em café (Coffea arabica L.)
(Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia / Universidade de São Paulo, 2004-04-29) Malerbo-Souza, Darclet Teresinha; Nogueira-Couto, Regina Helena; Couto, Leoman Almeida; Souza, Julio César de
O presente experimento foi conduzido em Jaboticabal, SP, e teve como objetivos estudar uma cultura de café (Coffea arabica L., var. Mundo Novo), quanto à biologia floral, a freqüência e comportamento dos insetos na flor, testar o produto Bee-HereR (Hoescht Shering Agrevo do Brasil Ltda) quanto a sua atratividade para as abelhas Apis mellifera e verificar a produção de frutos com e sem a visita dos insetos. Para isso, foram verificados o tempo do desenvolvimento e quantidade de açúcar solúvel do néctar das flores; freqüência das visitações dos insetos, no decorrer do dia, por meio de contagem do número de insetos visitando as flores, a cada 60 minutos, das 8 às 17 horas, 10 minutos em cada horário; tempo (em segundos) e tipo de coleta (néctar e/ou pólen) dos insetos mais freqüentes; perda de botões florais; porcentagem de flores que se transformaram em frutos; tempo de formação e contagem dos grãos de café, observando-se a porcentagem de frutificação em flores visitadas ou não pelos insetos. Também foram realizados testes por pulverização utilizando-se o produto Bee-HereR , diluído em xarope e em água, em diferentes horários. A flor durou, em média, cerca de 3 dias desde sua abertura até o murchamento. A quantidade de açúcares do néctar apresentou diferença significativa entre os horários, sendo maior às 8 horas (em média, 102,18 ± 8,75 mg de carboidratos totais por flor). A abelha A. mellifera foi o inseto mais freqüente nas flores de café, coletando, principalmente, néctar no decorrer do dia. A perda de botões florais causada pelas chuvas foi, em média, 26,50 ± 11,70%. O tempo para a formação do fruto foi 6 meses e o número de frutos decorrentes do tratamento descoberto foi maior (38,79% e 168,38%, em 1993 e 1994, respectivamente) que do tratamento coberto. Apesar da eficiência do produto Bee-HereR ser afetada pelas condições climáticas, ele pode ser usado para atrair as abelhas A. mellifera na cultura.
O café sombreado da serra de Baturité, Ceará, Nordeste do Brasil: gestão ambiental, sustentabilidade e impactos eco-ssocioeconômicos
(Universidade do Vale do Itajaí, 2023-09-15) Ribeiro, Sofia Regina Paiva; Lima, Filipe Augusto Xavier; Loiola, Maria Iracema Bezerra
O café sombreado da serra de Baturité, uma das poucas plantações no Brasil que integram lavoura-floresta, configura-se como uma antítese ao modelo agrícola predominante em nosso país, em monocultivo. Conhecido como “café de Baturité”, é apreciado por ser originário da variedade típica da espécie arábica (Coffea arabica) sombreada, com produção realizada por pequenos produtores rurais familiares, de forma agroflorestal. Diante desse cenário, o presente artigo objetiva verificar o impacto da revitalização da cultura do café de sombra na serra de Baturité a partir de iniciativas voltadas para o turismo, preservação ambiental e desenvolvimento socioeconômico regional. O procedimento metodológico adotado contempla estudo bibliográfico, observação participante e entrevistas semiestruturadas, com fontes-chave. Para tanto, as informações foram catalogadas, analisadas e confrontadas através da triangulação dos dados. Os resultados evidenciam que a cafeicultura, inserida na região há dois séculos (1822-2022), se encontra em fase de revitalização. Essa revalorização do cultivo, agora com conhecimentos empírico e técnico, vem contribuindo para minimizar o impacto antrópico na prática agrícola serrana, ampliar a gestão socioambiental nas propriedades rurais (onde o café se tornou um vetor de desenvolvimento sustentável) e fomentar a economia regional, como se observa a partir das ações voltadas para o ecoturismo, o empreendedorismo rural e a economia circular.
Selection of genotypes of Coffea arabica for drought tolerance based on anatomical and physiological characteristics
(Instituto de Pesquisas Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro, 2025-03-31) Santos, Cyntia Stephânia dos; Freitas, Ana Flávia de; Silva, Glauber Henrique Barbosa da; Tavares, Maria Clara dos Santos; Carvalho, Milene Alves de Figueiredo; Santos, Meline de Oliveira; Carvalho, Gladyston Rodrigues; Silva, Vânia Aparecida
Climate change affects crop productivity, with forecasts for the coming years pointing to increased temperatures and changes in rainfall distribution. This paper aimed to identify genotypes of Coffea arabica that are potentially drought-tolerant. Seven germplasm genotypes of Timor Hybrid were evaluated in comparison to two cultivars considered as sensitive and drought-tolerant. These were submitted to two water treatments, the first maintaining water availability and the second with complete suspension of irrigation. The physiological characteristics analyzed were gas exchange and predawn leaf water potential. For leaf anatomy, characteristics of the leaf lamina, conductive vessels and stomata were evaluated. It was found that some genotypes were able to maintain gas exchange even under low water availability. For these genotypes, the analysis of leaf anatomy presented an increase in cuticle thickness on the adaxial face, in the relationship between polar and equatorial diameters of stomata, in addition to a lower vulnerability index. A positive relationship was observed between adaxial phase cuticle thickness and water use efficiency. The Timor Hybrid UFV 377-21, UFV 376-31 and the cultivar IPR100 were the highlights among the genotypes analyzed, which presented adaptations that allowed the maintenance of the hydric status in the initial development phase.